How to Sing Better: The Areas of the Voice

We can think of the voice as divided into sections differentiated by changes in TA/CT balance and resonance activity as pitch ascends.
Singers feel sympathetic vibration differently in each of these areas of the voice.
LOWER REGISTER: Women below Eb4; Men below Bb3.
In the lower register, sympathetic resonance sensation is felt in the chest cavity and the TA muscles are very active. This area is known as modal register, mode 1, lower register, or chest voice. The vocal folds meet at the bottom of the depth of the fold and the vocal folds are squared.
The vocal quality is harmonically rich and speech-like. In the lower register, the body of the fold is tensed and the cover of fold including the ligament is relaxed. The TA muscles regulate vocal fold tension.
Male [ɑ] Vowel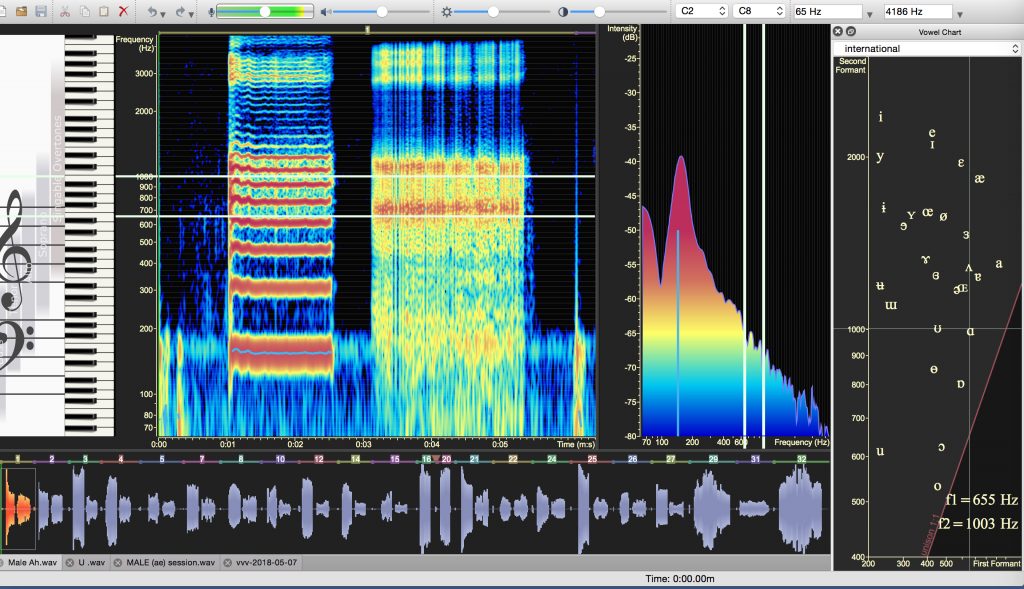
Here the male contemporary tenor sang the pitch in his lower register or chest voice. His vocal folds were firmly adducted, so you can see the presence of many strong harmonics above the fundamental frequency; they are fairly close together because the pitch is low. Vowel formants for the [ɑ] vowel: F1 is vibrating at 655 HZ, and F2 is vibrating at 1003 Hz.
APPROACH TO FIRST BRIDGE: Women Eb4-G4; Men B3-D4
In the approach to the first bridge area, sympathetic resonance sensation is felt in the chest cavity; the resonance strategy is F1/H2. This area is known as modal, mode 1, lower register, or chest voice. The vocal folds meet at the bottom of the depth of the fold and the vocal folds are squared.
The vocal quality is powerful and speech-like. The body of the fold is tense and the mucosa is slack. The F1/H2 resonance strategy becomes a yell if continued upward. To transition to the mix at the top of this area, the singer must begin to decrease TA muscle activity and resist the temptation to increase air pressure.
Male Approach to Primo Passaggio [ɑ]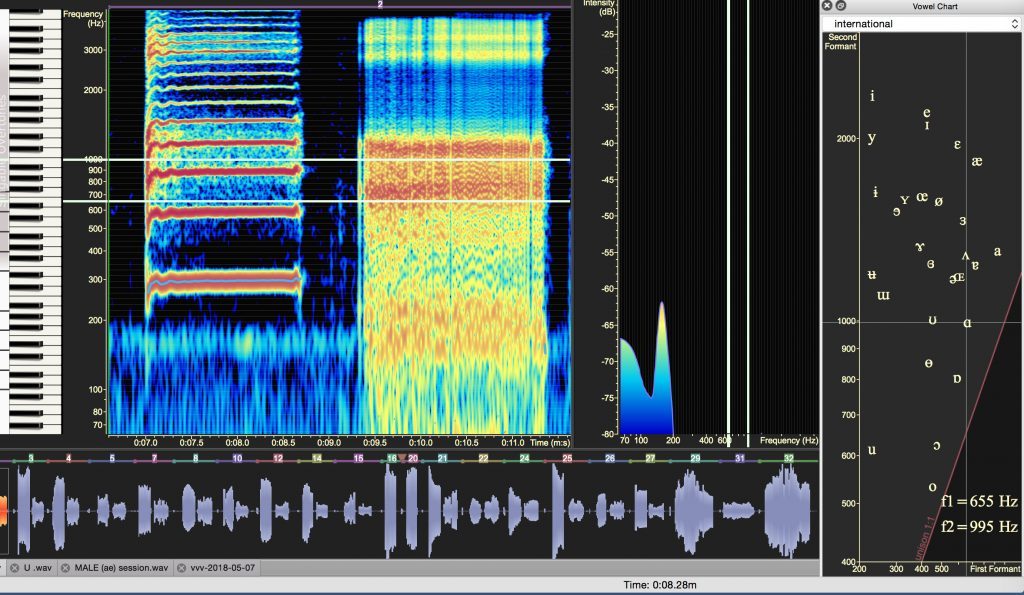
MIDDLE MIX: Women Ab4-Db5; Men Eb4-Ab4
In the middle mix area, sympathetic resonance sensation is felt in the mouth, mask, and behind the soft palate (perception of split resonance). F2, the second formant boosts nearby harmonics: F2/H3 (back vowels such as [o]), F2/H4 (front vowels such as [i] and [ae]).
TA and CT muscles are both activated but vocal fold contact is higher on the fold. The vocal folds become progressively longer and tauter due to the thyroid cartilage tilt; the TA muscles progressively decrease activity as pitch ascends.
This is the most destabilized area of the voice in the beginning mix singer, particularly if they habitually belt in this area.
The Middle Mix area has three modes or timbres, based on vocal fold adduction and compression, TA activity, harmonics boosted, and closed quotient.
- Falsetto (abducted vocal folds)
- Fluty Mix Timbre (also called head mix)
- Brassy Mix timbre (also called chest mix)
Mode Two, Fluty Mix, is used by the contemporary pop or musical theatre singer who wants a less edgy, more legit sound.
Male Middle Mix G4: Abducted Folds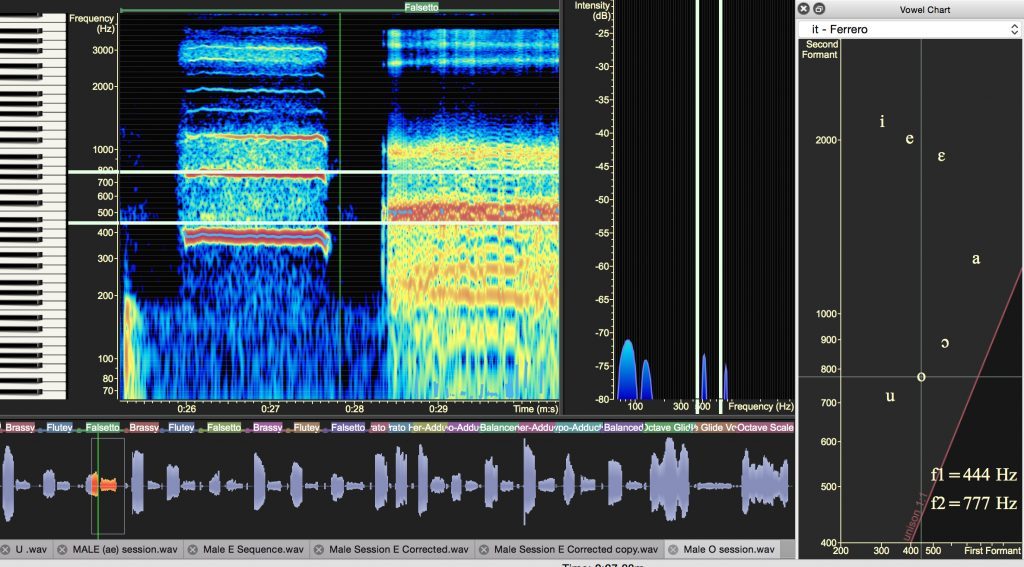
Male Middle Mix G4: Fluty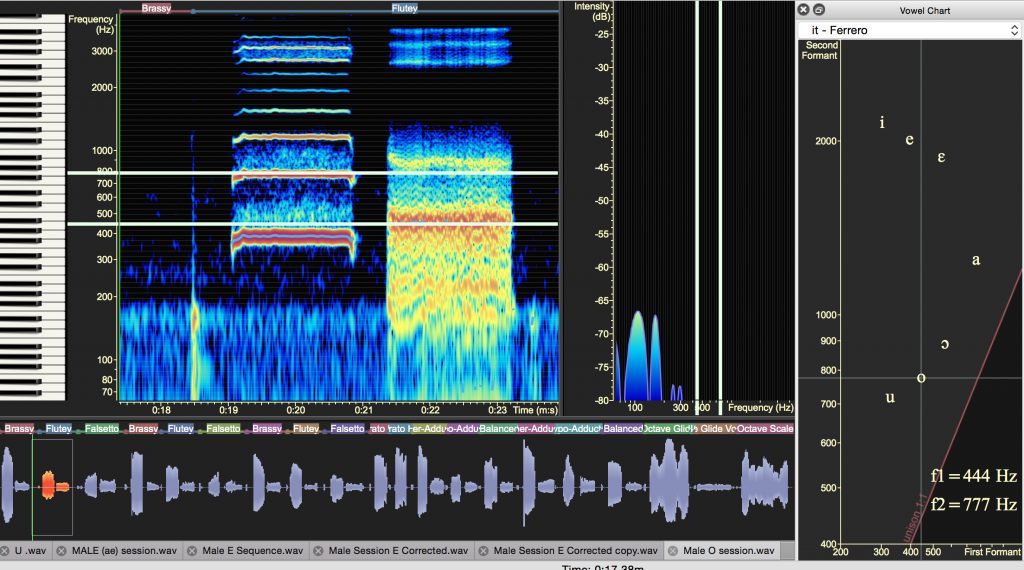
Male Middle Mix G4 Brassy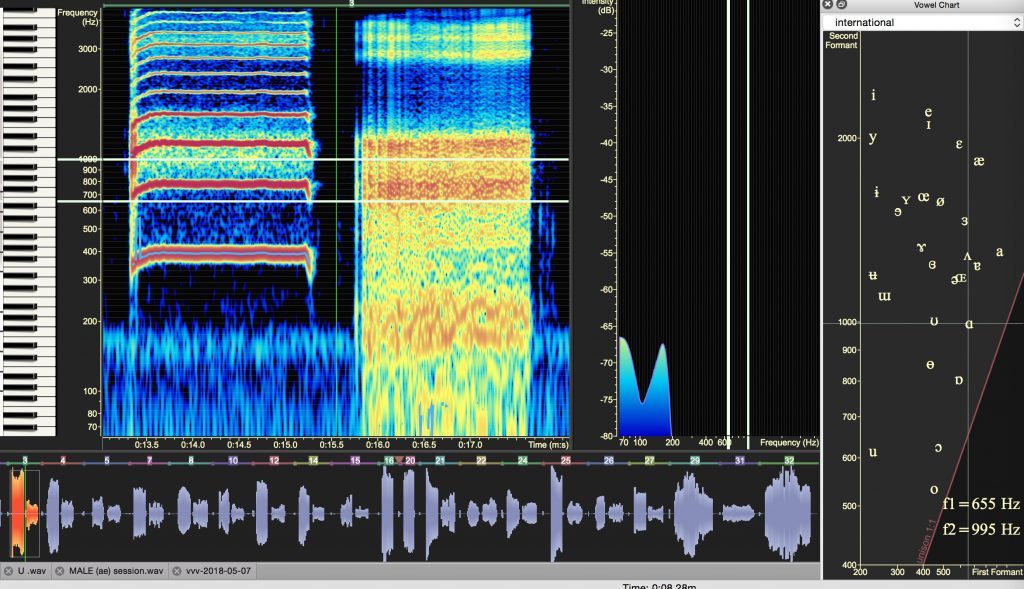
UPPER MIX: Women D5-Ab5; Men A4-D5
In the upper mix area, sympathetic resonance sensation is felt in the mouth, mask, and behind the soft palate (perception of split resonance). This phonation becomes increasingly CT muscle dominant with less bracing by TA muscles as pitch rises. F2, the second formant boosts nearby harmonics: F2/H3 (back vowels such as [o]), F2/H4 (front vowels such as [i] and [ae]). The vocal folds are progressively more lengthened and tauter and vocal fold contact is higher on the depth of the fold. As pitch ascends, the folds continue to elongate, decreasing muscle mass in vibration. The ligament begins to assume more of the tension bearing responsibility.
The Upper Mix area has three modes or timbres, based on vocal fold adduction and compression, TA activity, harmonics boosted, and closed quotient.
- Falsetto (abducted vocal folds)
- Fluty Mix Timbre (also called head mix)
- Brassy Mix timbre (also called chest mix)
Mode Two, Fluty Mix, is used by the contemporary pop or musical theatre singer who wants a less edgy, more legit sound.
Male Upper Mix: Brassy, Fluty, Abducted Folds (Falsetto)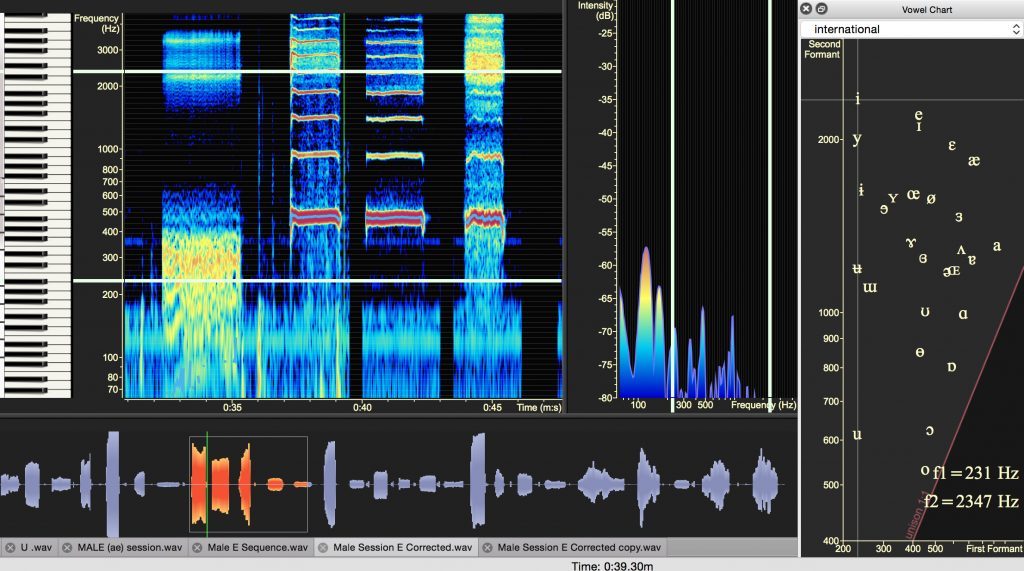
HEAD: Women A5-E6; Men D5-G5
As pitch ascends, the ligament begins to take more longitudinal tension of folds; vibration occurs in mucosa and ligament. There is little or no TA contraction. Sympathetic resonance sensation is felt in the head cavity. F1/H1 resonance strategy.
The ligament supports more of the longitudinal tension of folds; vibration occurs in mucosa and ligament. The vocal folds meet higher on the depth of the folds.
The F1/H1 resonance strategy is continued down to Eb4 or lower by the classical female singer.
The Legit Head (Woop) area has two modes, based on vocal fold adduction and compression and closed quotient:
- Falsetto (abducted vocal folds)
- Head (whoop)
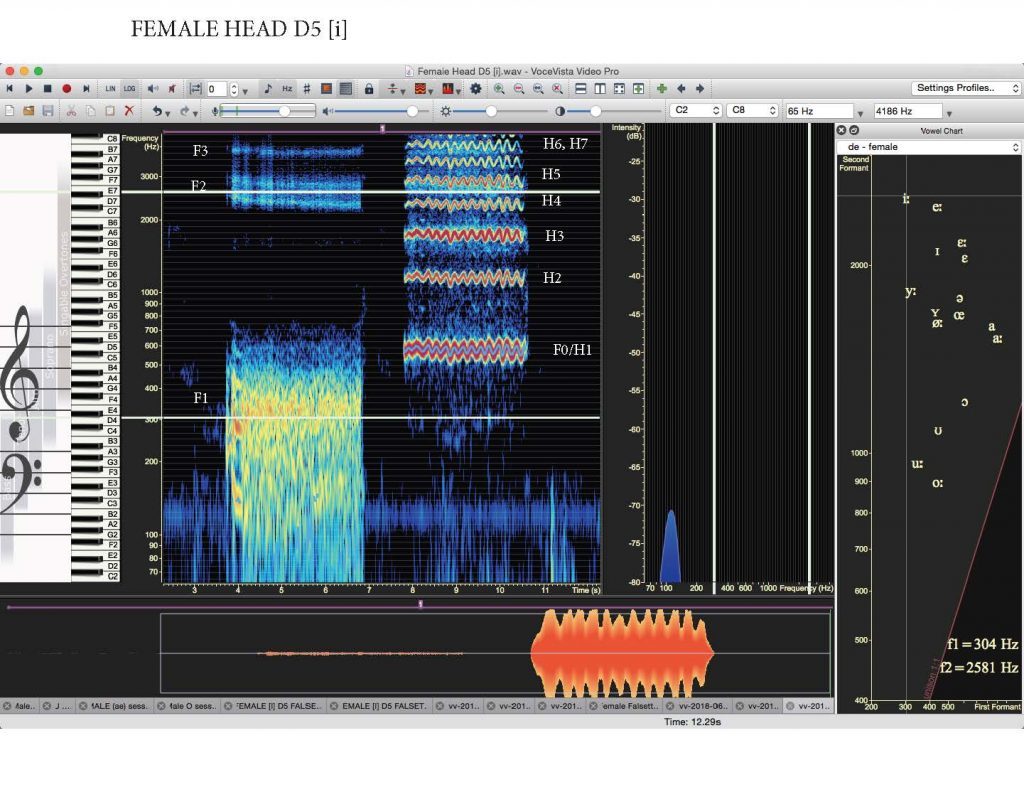
Female D5 Head Voice with Vibrato
WHISTLE (FLAGEOLET)
C6 (1,046.5 Hz) to D7 (2349.3 Hz). The vocal folds are stiffened and not vibrating along the entire length; the ligament supports longitudinal tension of the folds; vibration occurs only in the anterior (front) part of the folds.
The whistle is used mostly by female pop singers such as Mariah Carey, and a few men such as Adam Lambert.

If you would like to learn more about your voice AND learn to sing from home for less than you probably spend for lattes every month, check out our amazing YOU can Sing Like a Star online subscription courses for singers and voice teachers.
You can learn to sing with a self-study method- IF it's the right method. The ONLY method that can take you from beginner to professional is the YOU can Sing Like a Star online subscription course with over 600 recorded exercises.
This is the best method available and the ONLY method that takes you all the way from beginner to professional singer- for far less than the cost of in-person voice lessons!
Check this amazing course out at YOU can Sing Like a Star online subscription course.
If you are a voice teacher who wants to up your game, check out the YOU can be a Successful Voice Teacher online subscription course
With over 600 recorded exercises, including Riffs and Runs- Style, you don't need to be a great pianist or vocal stylist to be a great teacher!



